Air Bearing | Inspection
Stiffness measurement
Pressure the thrust plate with an air cylinder and measure the displacement on the opposite side.
Measurement of rotation accuracy
Measure a precision polished glass ball gauge placed on the thrust plate by optical sensors of X-Y axis and draw lissajous figure.
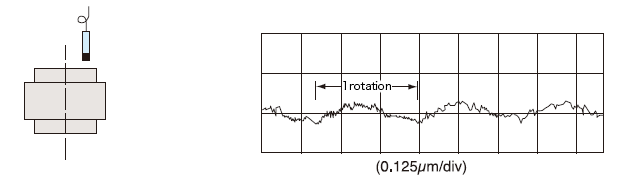
Measurement of the thrust plate (upper surface) runout
Measure the axial runout of the thrust plate (upper surface) with an optical sensor while rotating the thrust plate once.
Standard thrust plate (upper surface) runout accuracy is 1μm or less.
Optional thrust plate (upper surface) runout accuracy is 0.3μm or less.
Glossary
Rotation accuracy
Total indicator reading (TIR):Measure roundness of the axis of rotation per one rotation.
This accuracy directly affects the machining accuracy.
Stiffness
Axial stiffness:Power to displace the thrust plate 1μm in the axial direction.(unit:N/μm)
Radial stiffness:It is 1μm power to let you displace with a thrust plate in the radial direction.(unit:N/μm)
Common use load capacity
Axial direction:The power that can maintain the gap of the axial direction safely.(unit:N)
Radial direction:The power that can maintain the gap of the radial direction safely.(unit:N)
MAX load capacity
Axial direction:Limitation of the power that can maintain momentary the gap of the axial direction.(unit:N)
Radial direction:Limitation of the power that can maintain momentary the gap of the radial direction.(unit:N)
The thrust plate (upper surface) runout
The thrust plate (upper surface) runout of axial direction.
This accuracy directly affects the machining accuracy.



